Neben einer kleinen Adventsgeschichte und weihnachtlichen Matheaufgaben mit Lösungen gibt es für die Rätselfreudigen auch eine online "Schnitzeljagd" mit Preisen.
Wir freuen uns auf euch!
Einschreibeschlüssel: Lebkuchen

- Altwichtel: Kajetan Söhnen
- Trainer/in: Sebastian Hensel
- Trainer/in: Panagiotis Papadopoulos
- Trainer/in: Ralf Gerkmann
- Trainer/in: Simon Weinzierl
- Trainer/in: Andreas Leckner
- Trainer/in: Korbinian Meindl
Einschreibeschlüssel: 25WSSDM
- Trainer/in: Dirk Deckert
Mathematik I (Physik)
Einschreibeschlüssel: 25WSM1
- Trainer/in: Maralmaa Battsooj
- Trainer/in: Moritz Böger
- Trainer/in: Dirk Deckert
- Trainer/in: Leonard Petters
- Trainer/in: Junwoo Shin
- Trainer/in: Jago Silberbauer
- Trainer/in: Laurin Wolf
- Trainer/in: Werner Bley
- Trainer/in: Katharina Novikov
- Trainer/in: Werner Bley
- Trainer/in: Katharina Novikov
Course Description
In this seminar, we will explore machine learning methods built on (strictly) positive definite kernels - a powerful and mathematically well-understood class of models that form the foundation of many learning algorithms.
We begin with a review of strictly positive definite kernels and their key properties, including an introduction to reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces (RKHS) and related theoretical concepts.
Building on this foundation, we will study classical kernel-based algorithms such as support vector machines and kernel ridge regression, and discuss techniques for scaling them to large data sets.
The seminar will then turn to the intersection of kernel methods and deep learning, including topics such as the neural tangent kernel (NTK) and modern kernel-based approaches in deep learning like Recursive Feature Machines (RFMs).
Throughout the seminar, we will cover topics ranging from theoretical and mathematical foundations to practical and algorithmic aspects, giving students a broad view how kernel methods appear in both classical and modern machine learning.
Target Participants
Master students of Mathematics and Financial and Insurance Mathematics
Prerequisites
Some familiarity with machine learning and/or functional analysis is beneficial.
Registration key
ML
- Trainer/in: Tizian Wenzel
Diese Vorlesung bietet eine grundlegende Einführung in die Differential- und Integralrechnung einer Variablen. Sie lernen dabei, mathematische Sachverhalte präzise zu formulieren, den axiomatischen Aufbau der Mathematik zu verstehen und die grundlegenden Beweismethoden und Rechentechniken der Analysis anzuwenden. Das erworbene Wissen bildet die unverzichtbare Grundlage für alle weiterführenden Veranstaltungen.
Einschreibeschlüssel: BW2025
- Trainer/in: Holger Rauhut
- Trainer/in: Ulrich Terstiege
- Trainer/in: Simon Weinzierl
- Trainer/in: Tizian Wenzel
Einschreibeschlüssel: Tautologisch
Dieser Kurs richtet sich an angehende Studierende der Mathematik/Wirtschaftsmathematik sowohl im Bachelor als auch für das Lehramt Gymnasium. Ziel ist es, mathematische Grundfertigkeiten zu vermitteln und einzuüben, die für das Studium wichtig sind.
- Trainer/in: Ulrich Terstiege
- Trainer/in: Simon Weinzierl
- Trainer/in: Wiebke Bartolomaeus
- Trainer/in: Izak Cabanilla
- Trainer/in: Arinze Folarin
- Trainer/in: Leonardo Galli
- Trainer/in: Ulrich Terstiege
- Trainer/in: Juan Suarez Cardona
- Trainer/in: Tamas Makai
- Trainer/in: Konstantinos Panagiotou
- Trainer/in: Christian Hainzl
- Trainer/in: Riccardo Panza
- Trainer/in: Simon Gritschacher
- Trainer/in: Andreas Rosenschon
- Trainer/in: Lukas Böke
- Trainer/in: Matthias Nowinski
- Trainer/in: Ivo Sachs
- Trainer/in: Thomas Vogel
The lecture provides an introduction to stochastic calculus with an emphasis on the mathematical concepts that are later used in the mathematical modeling of financial markets.
In the first part of the
lecture course the theory of stochastic integration with respect to
Brownian motion and Ito processes is developed. Important results such
as Girsanov's theorem and the martingale representation theorem are also
covered. The first part concludes with a chapter on the existence and
uniqueness of strong and weak solutions of stochastic differential
equations.
The second part of the lecture course gives an introduction to the arbitrage theory of financial markets in continuous time driven by Brownian motion. Key concepts are the absence of arbitrage, market completeness, and the risk neutral pricing and hedging of contingent claims. Particular attention will be given to the the Black-Scholes model and the famous Black-Scholes formula for pricing call and put options.
If you wish to participate in the course, please sign up by sending an e-mail from your LMU e-mail address to Annika Steibel (steibel@math.lmu.de).
- Trainer/in: Miguel Armayor Martínez
- Trainer/in: Thilo Meyer-Brandis
- Trainer/in: Annika Steibel
- Trainer/in: Katharina Oberpriller
- Trainer/in: Ulrich Riegel
- Trainer/in: Adalbert Fono
- Trainer/in: Jianfei Li
- Trainer/in: Johannes Maly
- Trainer/in: Alessandro Sgarabottolo
Wir besprechen die Examensaufgaben vom letzten Herbst. Beginn am Dienstag 14.10.2025
Selbsteinschreibung mit Einschreibeschlüssel: semexana
- Trainer/in: Heribert Zenk
- Trainer/in: Stefan Kolek Martinez de Azagra
- Trainer/in: Mariia Seleznova
Goal: We study the fundamental mathematical concepts of quantum mechanics. In particular, we will discuss principles of quantum mechanics, self-adjoint operators, quadratic forms and Friedrichs extension, spectral theorems, Schrödinger operators, quantum dynamics, scattering theory, semiclassical analysis, and quantum entropy.
Audience : TMP-Master, Master students of Mathematics and Physics. Bachelor students will get "Schein" if pass the course.
Course homepage: https://www.math.lmu.de/~nam/MQM2526.php
- Trainer/in: Robert Helling
- Trainer/in: Thành Nam Phan
- Trainer/in: Stefan Kolek Martinez de Azagra
- Trainer/in: Mariia Seleznova
Wir werden typische Aufgabenstellungen beim Staatsexamen in Analysis behandeln,
Lösungsmethoden besprechen und evtl. noch etwas zugrunde liegende Theorie
wiederholen. Wir beginnen mit dem Themenbereich
Gewöhnliche Differentialgleichungen und
arbeiten uns dann zur Funktionentheorie durch.
Donnerstag 8.30-10 Uhr in B 005
Wir starten am Donnerstag den 17. Oktober 2024 um 8.30 Uhr mit
ganz "normalem" Aufgabenrechnen.
Einschreiben mit Einschreibeschlüssel: stexana
- Trainer/in: Heribert Zenk
Wir behandeln das Pauli-Fierz Modell für nichtrelativistisch beschriebene Materie, die an ein quantisiertes Strahlungsfeld gekoppelt ist. Wir untersuchen weitere Eigenschaften des bosonischen Fockraums, der bosonischen Erzeugungs- und Vernichtungsoperatoren und der Feldoperatoren, der zweiten Quantisierung von selbstadjungierten Operatoren -- die freie Energie der Photonen ist ein Beispiel dazu. Dies erlaubt den Hamiltonoperator des minimal gekoppelten Systems überhaupt genau hinschreiben zu können und dann die Selbstadjungiertheit für das UV- regularisierte Pauli-Fierz Modell zu zeigen.
Selbsteinschreibung mit Einschreibeschlüssel mqed
- Trainer/in: Heribert Zenk
Vorlesung: Montag 10-12 Uhr in H30 (Schellingstraße 4) und Donnerstag 14-16 Uhr in B138 (Theresienstraße 39)
Übung: Mittwoch 10-12 Uhr in B138
Ist
der dritte Teil der einführenden Mathematik Vorlesungen im Bachelor
Physik. Wir machen am 13. Oktober mit dem
Topologie Kapitel weiter. Dann gibt es Maß- und
Integrationstheorie und Differentialrechnung.
Selbsteinschreibung mit Einschreibeschlüssel m3p
- Trainer/in: Veronika Biber
- Trainer/in: Karl-Wilhelm Georg Bollweg
- Trainer/in: Cassian Hallinger
- Trainer/in: Kajetan Söhnen
- Trainer/in: Yexuan Wang
- Trainer/in: Heribert Zenk
Analysis und Lineare Algebra I
ist
die Mathematikvorlesung für das erste Semester im Mathematikstudium für
Lehramt Gymnasium (nach der Prüfungsordnung von 2022) am Dienstag 12-14
in B138, Mittwoch 14-16 in B138 und Donnerstag 10-12 in B138.
Übung ist am Freitag 12-14 Uhr in B138, in der die zuvor abgegebenen Übungsaufgaben besprochen werden. Bis
wir mit der Besprechung starten können, gibt es am Freitag -- also
sicher am 17.10.2025 -- noch zusätzliche Vorlesungen.
Beginn: 14.10.2025
- Trainer/in: Kajetan Söhnen
- Trainer/in: Heribert Zenk
Einschreibeschlüssel: DiffInt1W25
- Trainer/in: Erwin Schörner
- Trainer/in: Jago Silberbauer
Einschreibeschlüssel: LinAlg1W25
- Trainer/in: Panagiotis Papadopoulos
- Trainer/in: Erwin Schörner
Einschreibeschlüssel: ExamUF25W
- Trainer/in: Daniel Rost
- Trainer/in: Erwin Schörner
Einschreibeschlüssel: MiQWS25
- Trainer/in: Daniel Rost
Einschreibeschlüssel: Grund1WS25
- Trainer/in: Laura Paul
- Trainer/in: Daniel Rost
About this Lecture
This lecture discusses the interplay of Theory, Modelling, Numerical Methods and Implementation in Mathematical Finance.
All aspects learn from each other: one needs to understand the theory to build models and good implementations. Studying numerical experiments gives deeper theoretical insight. Using the computer to understand math can be fun!
We discuss how to build an industry-grade implementation of our models and allow future extensions while being efficient.
We discuss practical applications in the financial industry.
The lecture tries to be as self-contained as possible, but we will use some numerical methods developed in a previous course. We will start with a short recapitulation of the numerical methods needed for those who did not follow the last lecture. It is possible to consider most of these parts as “given” (“black box”). Don’t panic: We will assist you.
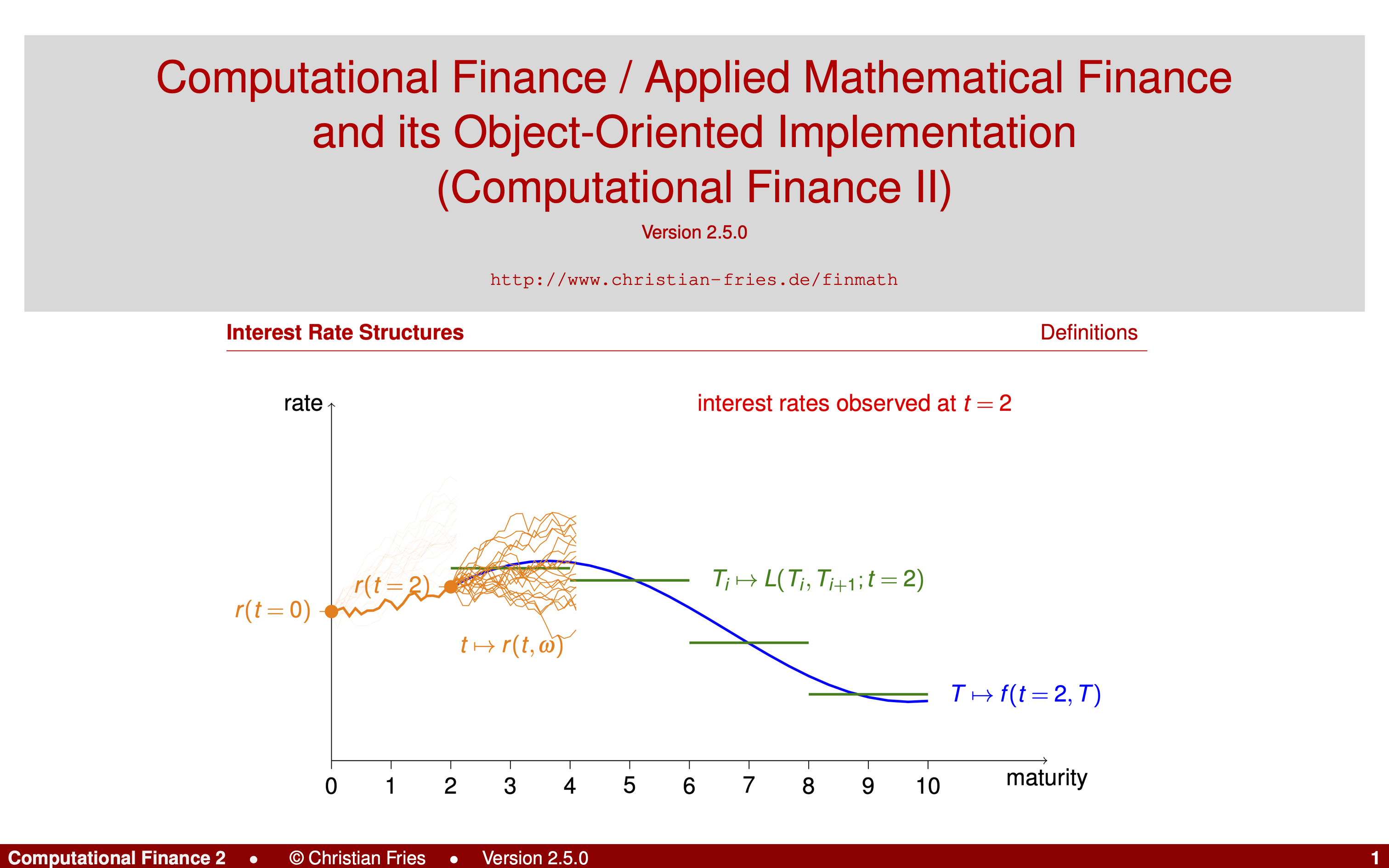
The lecture will discuss the theory and application of some prominent methods and models from mathematical finance. We focus on interest rate and hybrid models with high relevance for the financial industry. In an excursion, we consider a climate model (DICE), extend it and combine it with our interest rate models.
We will then use our implication to gain a deeper understanding of the theoretical properties of the model.
If time permits, we conclude the lecture by discussing running our models in a cloud.
Tentative Agenda
- Recapitulation of Numerical Methods (Monte-Carlo Method, SDEs, etc.)
- Interest Rates, Linear Interest Rates Products
- Multiple Interes Rate Curve Modelling and its Implementation
- Interest Rate Options, Convexity Adjustment
- Discrete Term-Structure Models (formerly known as LIBOR Market Models) and their Implementation
- Model Calibration
- Valuation of Complex Derivatives
- Object Oriented Implementation, Definition of Model Interfaces
- Short Rate Models and their Implementation
- Climate Models
- Numerical Methods in the Context of Mathematical Finance
- Model Calibration: Optimization and Root-Finding
- Correlation Modelling: Prinzipal Component Analysis and Factor Reduction, Regression Methods
- IT Implementation of Models, e.g. in the Cloud
The lecture covers the object oriented implementation of the algorithms and using modern software development tools.
As part of the implementation of the models and the valuation algorithms, the lecture will discuss some of the latest standards in software development.
- revision control systems (git)
- unit-testing (junit)
- build management (maven, gradle)
- continuous integration (TravisCI, Jenkins)
Implementation will be performed in Java (Eclipse, IntelliJ)
- Trainer/in: Christian Fries
- Trainer/in: Alessandro Sgarabottolo
- Trainer/in: Niklas Weber
- Trainer/in: Rupert Frank
- Trainer/in: Peter Madsen
- Trainer/in: David Scholz
- Trainer/in: Yaojun Wang
Einschreibeschlüssel: Num2526
- Trainer/in: Paul Pfeiffer
- Trainer/in: Peter Philip
Einschreibeschlüssel: AnIS2526
- Trainer/in: Sakirudeen Abdulsalaam
- Trainer/in: Julius Hallmann
- Trainer/in: Peter Philip
- Trainer/in: Katharina Novikov
- Trainer/in: Andreas Rosenschon
Course Description
In this seminar, we will analyse one-dimensional stochastic differential equations (SDEs) driven by a Brownian motion. To this end, a short review of semimartingales, stochastic integrals and Itô's formula will be discussed. Under Lipschitz conditions on the drift and diffusion coefficients of the SDE, we will derive unique strong solutions. In particular, we will recover the Brownian bridge and the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process as solutions of affine SDEs.
Target Participants
- Master students of Mathematics and Financial and Insurance Mathematics
Pre-requisites
- Probability theory and measure and integration theory
Registration key
- SDE
- Trainer/in: Alexander Kalinin
Course Description
In this reading course, we will study stochastic processes in continuous time that happen to be sub- or supermartingales. In particular, this includes martingales. After proving Doob's maximal inequalities and stopping theorem, we will derive the quadratic variation of a local martingale. As a result, we will be able to understand the notion of a semimartingale.
Target Participants
- Master students of Mathematics
Pre-requisites
- Probability theory and measure and integration theory
Registration key
- martingales
- Trainer/in: Alexander Kalinin
Course Description
In this lecture, we will consider various classes of stochastic processes that may differ in their state spaces and underlying index sets with a special focus on Gaussian, Lévy and Markov processes. In summary, the lecture will be divided into three core topics: the construction, the path behaviour and the probabilistic analysis of general stochastic processes.
Target Participants
- Master students of Mathematics and Financial and Insurance Mathematics
Pre-requisites
- Probability theory and measure and integration theory
Registration key
- Processes
- Trainer/in: Alexander Kalinin
Die
Problemlabs bieten einen Raum zum gemeinsamen Arbeiten und Lernen. Ob
ihr Hausaufgaben bearbeitet oder nochmal das Skript nacharbeitet ist
dabei ganz euch überlassen.
An mehreren Terminen wird der Raum von
ehrenamtlichen Tutor:Innen aus höheren Semestern betreut, so dass ihr
bei Fragen oder Unklarheiten die nötige Unterstützung bekommt.
Anmeldeschlüssel: NoProblem
- Trainer/in: Sarah Haselbeck
- Trainer/in: Kajetan Söhnen
Blockkurs in der vorlesungsfreien Zeit, in dem die Grundlagen des Textsatzsystems LaTeX und speziell die Erstellung mathematischer Texte behandelt werden. Nähere Informationen zum Ablauf finden Sie auf der Webseite des Kurses.
Einschreibeschlüssel: LaTeX2025
- Trainer/in: Mechtild Callies
The module is a continuation of the classical part of Mathematical Statistical Physics from summer. We'll cover some advanced topics, starting with
- Reflection positivity & proof of orientational symmetry breaking in dimensions 3 and higher
- Cluster expansions - a perturbative technique, related to but easier than Feynman diagrams
- Pirogov-Sinai theory: a technique for proving first-order phase transitions at low temperature. The technique builds on ideas of the Peierls argument but is considerably more involved.
- Trainer/in: Sabine Jansen
Passwort: cantelli
- Trainer/in: Sabine Jansen
- Trainer/in: Fabian Nolte
Inhalt der Vorlesung ist eine Einführung in die Optimierung in - vornehmlich - endlicher Dimension. Wichtige Themen und Inhalte sind unter anderem:
Konvexität, Lineare Programme und ihre Standardformen, Existenz von Lösungen für lineare Programme, Dualitätstheorie für lineare Programme, das Simplexverfahren, Formulierung und Existenz von Lösungen konvexer Optimierungsprobleme, duale Darstellung konvexer Funktionen und die Kuhn-Tucker-Theorie.
- Trainer/in: Julian Becker
- Trainer/in: Ari-Pekka Perkkiö
Signing up opens 06. October 2025.
- Trainer/in: Marco Schmid
- Trainer/in: Thomas Sørensen
- Trainer/in: Tamas Makai
- Trainer/in: Paula Reichert-Schürmer
- Trainer/in: Paula Reichert-Schürmer
- Trainer/in: Alois Wohlschlager
- Trainer/in: Jonas Beyrer
- Trainer/in: Christian Lange
- Trainer/in: Jonas Beyrer
- Trainer/in: Christian Lange
- Trainer/in: Bernhard Leeb
In dieser Vorlesung behandeln wir gemeinsam die Grundlagen der (Hochschul-)Mathematik.
Thematisch beginnen wir bei fundamentalen Begriffen wie Mengen und Abbildungen, sprechen dann über zentrale Begriffe der Analysis wie Folgen und Stetigkeit und widmen uns am Ende Ableitungen und Integrale.
Die Veranstaltung richtet sich an Studierende verschiedener Bachelorstudiengänge, wie z.B. Geowissenschaften und Informatik mit großem Nebenfach.
Anmeldeschlüssel: MfNW
- Trainer/in: Fabian Darabi Far
- Trainer/in: Kajetan Söhnen
Gute Tutorinnen und Tutoren sind essentiell für eine gute Lehrveranstaltung, insbesondere bei gut besuchten Vorlesungen. Aber was zeichnet eine gute Tutorin aus und worauf sollte man als Tutor achten?
Zusammen mit Ihnen wollen wir in mehreren Workshops über
Herausforderungen, Chancen und bewährte Methoden bei Tutorien und
Korrektur sprechen.
Einschreibeschlüssel: Tutor
- Trainer/in: Milena Damrau
- Trainer/in: Sebastian Hensel
- Trainer/in: Alexander Rachel
- Trainer/in: Paula Reichert-Schürmer
- Trainer/in: Kajetan Söhnen